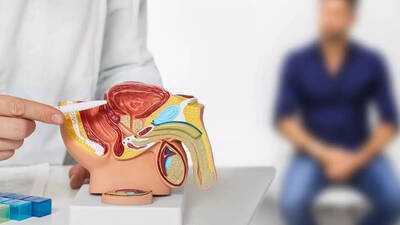
Prostate cancer is a disease that develops in the prostate gland, a small gland in men responsible for producing seminal fluid that nourishes and transports sperm. It usually grows slowly, but some forms can be more aggressive and spread quickly if not detected early. While age, family history, and ethnicity are uncontrollable risk factors, lifestyle choices can play a major role in prevention. Eating a nutrient-rich diet, staying physically active, and avoiding habits such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can help maintain hormonal balance and support prostate health, reducing the likelihood of developing prostate cancer.
10 effective ways to reduce the risk of prostate cancer
According to a study published in the effective strategies for reducing the risk of prostate cancer include lifestyle changes, dietary adjustments, and the careful use of preventive medications. The research highlights the importance of maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, and following a plant-based diet. Here are 10 evidence-based strategies to help protect prostate health:
1. Eat a plant-based, high-fibre diet
A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes provides fibre, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support overall health and may protect against prostate cancer. Fibre aids digestion and helps regulate hormone levels, which can influence cancer risk. Incorporate leafy greens, beans, lentils, and whole grains into daily meals, aiming for at least five portions of fruits and vegetables each day.
2. Include lycopene-rich foods
Lycopene, a powerful antioxidant found in tomatoes, watermelon, and pink grapefruit, may help reduce the risk of prostate cancer by neutralising free radicals that can damage cells. Cooking tomatoes in olive oil enhances the absorption of lycopene. Regularly adding tomato-based sauces, soups, or stews to your diet can increase your intake of this beneficial compound.
3. Consume cruciferous vegetables
Vegetables like broccoli, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts, and kale contain sulforaphane and other compounds that may have anti-cancer properties. These compounds help support detoxification processes in the body, reduce inflammation, and may inhibit the growth of cancer cells. Including these vegetables several times a week can provide long-term protective benefits.
4. Eat berries and pomegranate
Berries such as blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries, along with pomegranate, are rich in antioxidants and polyphenols. These compounds can reduce oxidative stress and inflammation, which are linked to cancer development. Snacking on berries, adding them to cereals, or drinking pomegranate juice regularly may help protect prostate cells from damage.
5. Maintain a healthy weight
Being overweight or obese is linked to more aggressive forms of prostate cancer. Excess body fat can increase inflammation and alter hormone levels, contributing to cancer progression. Maintaining a healthy weight through a combination of diet and regular exercise not only lowers cancer risk but also supports heart health, blood sugar control, and overall longevity.
6. Exercise regularly
Regular physical activity reduces cancer risk by improving immune function, lowering inflammation, and helping maintain a healthy weight. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity activity per week, such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling. Resistance training and stretching exercises can also improve muscle mass, support metabolic health, and enhance overall wellbeing.
7. Limit red and processed meats
High consumption of red meats and processed meats like bacon, sausages, and ham has been linked to increased prostate cancer risk. These meats may contain compounds formed during cooking or processing that promote cancer development. Replace some red meat servings with fish, poultry, or plant-based proteins, and try cooking methods like steaming, poaching, or baking instead of grilling or frying.
8. Moderate alcohol consumption
Alcohol, particularly in excess, can increase the risk of several cancers, including prostate cancer. Limiting alcohol intake to recommended guidelines or avoiding it altogether can reduce risk. Choosing water, herbal teas, or natural fruit juices as alternatives helps maintain hydration and supports liver and overall health.
9. Consider genetic risk
Men with a family history of prostate cancer or who carry higher genetic risk factors should be extra vigilant. Early discussions with healthcare providers about screening options, such as PSA tests or MRI scans, can help detect changes early when treatment is most effective. Awareness of personal risk factors allows for tailored prevention strategies.
10. Regular check-ups and awareness
Regular medical check-ups allow early detection of any changes in prostate health. Men should be aware of symptoms such as difficulty urinating, blood in urine or semen, or pelvic discomfort, and seek medical advice promptly if they occur. Combining proactive screenings with lifestyle and dietary measures creates a comprehensive approach to reducing risk.
Disclaimer:
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a healthcare professional before making any changes to your diet, medication, or lifestyle.
Also read |
 Prostate cancer is a disease that develops in the prostate gland, a small gland in men responsible for producing seminal fluid that nourishes and transports sperm. It usually grows slowly, but some forms can be more aggressive and spread quickly if not detected early. While age, family history, and ethnicity are uncontrollable risk factors, lifestyle choices can play a major role in prevention. Eating a nutrient-rich diet, staying physically active, and avoiding habits such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can help maintain hormonal balance and support prostate health, reducing the likelihood of developing prostate cancer.
Prostate cancer is a disease that develops in the prostate gland, a small gland in men responsible for producing seminal fluid that nourishes and transports sperm. It usually grows slowly, but some forms can be more aggressive and spread quickly if not detected early. While age, family history, and ethnicity are uncontrollable risk factors, lifestyle choices can play a major role in prevention. Eating a nutrient-rich diet, staying physically active, and avoiding habits such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can help maintain hormonal balance and support prostate health, reducing the likelihood of developing prostate cancer.