
First, researchers from the Department of Science and Technology’s (DST) independent Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA) have shown that shock waves are produced when a radio jet from a dwarf galaxy interacts with interstellar space.
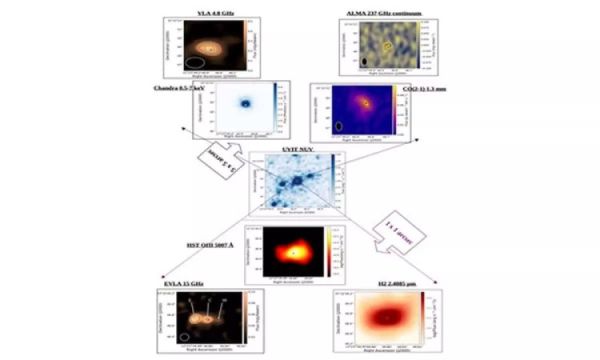
The group discovered that the radio jet emanated from the black hole known as the Active Galactic Nuclei (AGN) in the galaxy’s center, NGC 4395. It is well known that AGN form their galaxies and release brilliant winds and jets.
The brilliant jet had tiny spatial-scale interactions with the surrounding interstellar medium, roughly or equal to 30 light years. The dwarf galaxy is located around 14 million light years away.
In order to determine the interaction around the black hole, the scientists merged data from radio to X-ray wavebands from the galaxy NGC 4395. Their findings were reported in a publication in the Astrophysical Journal.
Lead author Payel Nandi, an IIA doctorate student, stated, “We decided to investigate how the radio jet from a small black hole interacts with the gas in a dwarf galaxy called NGC 4395.”
The group examined data from the UltraViolet Imaging Telescope (UVIT) on board AstroSat, India’s first dedicated space observatory that was launched by ISRO in 2015. They also used optical and X-ray data from the Hubble Space Telescope and Chandra, as well as data from Gemini-North and Chandra.
The results revealed a distinct radio structure with a black hole-centered core that resembled a bipolar jet.
Prof. C. S. Stalin of IIA, who co-authored the work, said, “This jet is relatively weak, but our multi-wavelength analysis of this 30-light-year region showed that the jet is interacting with the surrounding gas, and possibly causing shock waves to propagate through it.”
The radio jet’s route is precisely matched by the light released by the ionized oxygen in the optical band, the molecular hydrogen in the infrared, and the X-ray emission.
The investigation revealed “strong evidence for an outflow of material carried by jet into the surrounding medium,” according to Nandi.