A brain disease caused has been found in patients who have not for the first time.
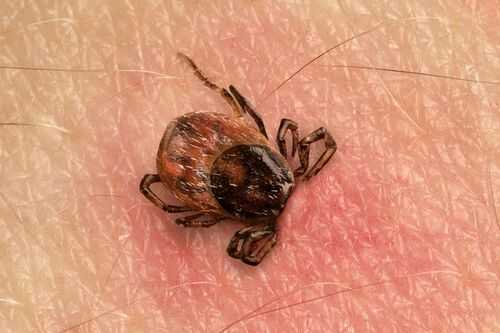
The symptoms of encephalitis (TBEV) are often similar to those of including a high fever, headache, stiff neck and reduced consciousness. It is most commonly caught by people who have visited the likes of , , Japan and other nations in Europe.
Last year a case was confirmed in Yorkshire and was also detected in Hampshire, Dorset, and Norfolk. Now it has been confirmed in a case in Britain where the patient has not been abroad for the first time, proving it is spreading locally.
READ MORE:
A study in reads: “Doctors should now consider whether TBE could be the cause in patients who present with unexplained encephalitis. Current public health campaigns encourage everyone to be tick aware with the aim to try and prevent Lyme disease transmission. These campaigns should also now include TBEV.
“Previously, TBEV was considered absent from the UK, although LIV is endemic in the UK, causing disease in sheep, cattle and other livestock and occasional human infections. Recognising the potential risk for TBEV ingress into the UK, systematic surveillance was conducted in ticks and sentinel animals, such as deer. The surveillance programme tested for TBEV antibodies in culled deer in England and , and results were used to identify areas for focused tick collection.”
Anyone who feels unwell after a tick bite should seek GP advice and urgent medical attention if you, or someone you know, have symptoms of meningitis. Dr Meera Chand, Deputy Director at the UK Health Security Agency, said: “Our surveillance suggests tick borne encephalitis virus is very uncommon in the UK and the risk to the general population is very low.
“Ticks also carry various other infections, including Lyme disease, so take steps to reduce your chances of being bitten when outdoors in areas where ticks thrive, such as moorlands and woodlands, and remember to check for ticks and remove them promptly.”
List of meningitis symptoms:
Severe headache
Stiff neck
Pain looking at bright lights
Develops neurological symptoms:
Has a fit (seizure), if not known to be epileptic
Sudden confusion or change in behaviour
Weakness or loss of movement in arms and legs
Facial dropping, change in vision or slurred speech