How Sunscreen Went from Optional to Essential: Reasons Why You can't Skip it Anymore!

Once considered an optional beach accessory, sunscreen has now become a daily skincare essential. Dermatologists and health experts stress its importance, not just for preventing sunburns but also for protecting against long-term skin damage and even life-threatening diseases like skin cancer. But how did sunscreen evolve from an occasional summer necessity to an everyday must-have? This article explores the importance of sunscreen, its different types, how to use it correctly, and the consequences of neglecting it.
The Importance of Sunscreen 
Sunscreen is crucial for shielding the skin from the harmful effects of ultraviolet (UV) radiation. The sun emits two main types of UV rays: UVA and UVB. UVA rays penetrate deep into the skin, leading to premature aging, wrinkles, and hyperpigmentation. UVB rays, on the other hand, are responsible for sunburns and can cause direct damage to DNA, increasing the risk of skin cancer.
Regular use of sunscreen provides the following benefits:
 Prevents Skin Cancer
Prevents Skin Cancer: Prolonged UV exposure is the leading cause of skin cancer, including melanoma, the deadliest form. Studies show that daily use of sunscreen significantly lowers the risk.
Delays Skin Aging: UV rays break down collagen and elastin, causing premature wrinkles and sagging. Sunscreen helps maintain a youthful appearance.
Reduces Hyperpigmentation: Dark spots and uneven skin tone often result from sun exposure. Sunscreen prevents further discoloration and maintains an even complexion.
Protects Against Sunburns: Sunburns cause painful skin damage and increase the risk of long-term skin issues.
Types of Sunscreens

There are two primary types of sunscreens: chemical and physical (mineral). Understanding their differences can help you choose the best option for your skin type and lifestyle.
1. Chemical Sunscreen Chemical sunscreens contain active ingredients such as oxybenzone, avobenzone, and octinoxate, which absorb UV radiation and convert it into heat, releasing it from the skin. These sunscreens are lightweight, blend easily, and are ideal for everyday wear under makeup. However, some people with sensitive skin may experience irritation from certain chemical filters.
2. Physical (Mineral) Sunscreen
Physical sunscreens contain natural minerals like zinc oxide and titanium dioxide, which create a barrier that reflects UV rays away from the skin. These are generally gentler, making them ideal for sensitive skin and children. However, they can leave a white cast on darker skin tones, though newer formulations aim to minimize this effect.
How to Use Sunscreen Properly

Applying sunscreen correctly is just as important as choosing the right type. Here’s how to maximize its effectiveness:
Apply Generously: Use at least a nickel-sized amount for the face and about a shot glass (two tablespoons) for the body.
Use It Every Day: Sunscreen should be applied daily, regardless of the weather or season. UV rays penetrate clouds and even glass windows.
Reapply Frequently: Sunscreen wears off due to sweat, water, and natural skin oils. Reapply every two hours, or more often if swimming or sweating.
Apply 15-30 Minutes Before Sun Exposure: This allows the sunscreen to absorb properly and form a protective barrier.
Don’t Forget Key Areas: Ears, lips, neck, hands, and feet are often overlooked but are equally prone to sun damage.
What Happens If You Don’t Use Sunscreen? 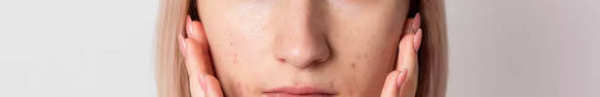
Neglecting sunscreen can have severe short- and long-term consequences. Here’s what can happen:
Sunburns: The immediate effect of unprotected sun exposure is painful redness, blistering, and peeling skin. Severe sunburns can even lead to hospitalization.
Premature Aging: Without sunscreen, UV rays accelerate the breakdown of collagen, leading to wrinkles, sagging skin, and age spots.
Hyperpigmentation: Uneven skin tone, dark spots, and melasma can develop due to repeated sun exposure.
Weakened Immune System: UV exposure can suppress the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight infections.
Increased Risk of Skin Cancer: The most dangerous consequence of skipping sunscreen is a higher likelihood of developing skin cancer. According to the Skin Cancer Foundation, one in five Americans will develop skin cancer by the age of 70, and consistent sunscreen use can reduce this risk by 50%.
The transition of sunscreen from an occasional luxury to a daily necessity is backed by scientific evidence and medical recommendations. With rising cases of skin cancer, premature aging, and sun-induced damage, sunscreen is no longer optional—it’s essential. By understanding its importance, choosing the right type, and using it properly, you can protect your skin and maintain its health for years to come. So, the next time you step outside, make sure you’ve applied your sunscreen—your skin will thank you!
Frequently Asked Images (FAQs):
Is sunscreen necessary for a skincare routine?
Yes, sunscreen is essential for protecting the skin from UV damage, premature aging, and skin cancer.
When was sunscreen first introduced?
Modern sunscreen was first introduced in the 1930s, with early commercial versions appearing in the 1940s.
What stage of skincare do you apply sunscreen to?
Sunscreen should be the last step of your skincare routine, applied after moisturizer and before makeup. Explore the latest trends and tips in , , , and at .
 Once considered an optional beach accessory, sunscreen has now become a daily skincare essential. Dermatologists and health experts stress its importance, not just for preventing sunburns but also for protecting against long-term skin damage and even life-threatening diseases like skin cancer. But how did sunscreen evolve from an occasional summer necessity to an everyday must-have? This article explores the importance of sunscreen, its different types, how to use it correctly, and the consequences of neglecting it.
Once considered an optional beach accessory, sunscreen has now become a daily skincare essential. Dermatologists and health experts stress its importance, not just for preventing sunburns but also for protecting against long-term skin damage and even life-threatening diseases like skin cancer. But how did sunscreen evolve from an occasional summer necessity to an everyday must-have? This article explores the importance of sunscreen, its different types, how to use it correctly, and the consequences of neglecting it.




