Moreover, if even after brushing twice a day, flossing daily, and using a fancy mouthwash, your bad breath or bleeding gums are not budging, then it might the time to check your gum-gut connection.
To know how gut health might affect gum health (Periodontal Disease), we asked
Dr Jayendra Shukla, Consultant, Gastroenterology, Apollo Hospitals Lucknow and Dr Siddharth Shelat, Consultant, Dental Sciences, Apollo Hospitals Lucknow, to share their expertise.
How Can Poor Gut Health Be Linked to Oral Issues?
According to Dr Shelat, "Your mouth is the entry point to the digestive tract, and its health is closely tied to the balance of bacteria throughout the body, especially the gut."
Dr Shelat Tells How the Gut Can Influence Oral Issues:
- Bacterial Overgrowth: An unhealthy gut may lead to an overgrowth of harmful bacteria, which can travel upward and influence the oral microbiome.
- Inflammatory Signals: Chronic inflammation in the gut (due to poor diet, stress, or disease) can trigger systemic inflammation, including the gums.
- Nutrient Absorption: Poor gut function reduces the absorption of essential nutrients like vitamin C and zinc, both crucial for gum health and tissue repair.
"Patients with leaky gut, IBS, or chronic gut inflammation often experience oral symptoms like recurring gum infections or persistent bad breath," adds Dr Shelat.
Do Oral Problems Indicate Poor Gut Issues?
Dr Shelat explained it as, "Your oral cavity has its own microbiome, and any disruption in the gut can throw the oral bacteria out of balance too. When we notice an unusual spike in pathogenic bacteria in the mouth, like Porphyromonas gingivalis (linked to gum disease), we sometimes trace it back to poor gut health."
Important Indicators to Look Out for:
- Constant bad breath which does not improve with dental cleaning.
- The frequent inflammation of the gums despite the lack of tartar formation.
- Mouth ulcers or a coated tongue may mean or the inability of the organism to detoxify.
"Nowadays, many dentists start referring their patients to a gastroenterologist to diagnose and treat them with a more extensive approach when oral problems appear resistant to the regular procedure," added Dr Shelat.
Dental Symptoms to Pay Attention to
According to Dr Shelat, "Although the majority of oral problems are related to local causes, there are some gastric red flags that might cause oral problems too." These symptoms include:
- Constant bleeding gums, particularly, without any indication of scaling accumulation.
- Halitosis, or bad breath, despite washing the mouth and using mouthwash.
- Chronic infections in the mouth or inability to heal point to the .
General ulcers of the mouth or burning of the tongue, occasionally associated with .
"If a patient is getting all his dental treatments right and still sees no improvement, one should look for gut problems, such as SIBO, food intolerance, or nutrient deficiencies," advised Dr Shukla.
What is the Impact of Gut Dysbiosis on Oral Health, Particularly Breath and Gum Problems?
According to Dr Shukla, Sharma says, "Gut dysbiosis, a situation in which the number of bad bacteria is much higher as compared to good bacteria. This imbalance can cause fringe effects to the rest of the body, including the mouth."
Here's How:
- Toxins & Gases: Bad gut bacteria may emit stinking gases such as hydrogen sulfide or methane, which contribute to bad breath.
- Weakened Immune System: An irritable bowel suppresses the immune system, and this can predispose you to oral illnesses.
Do Oral Symptoms Get Better with the Treatment of Gut Problems such as Acid Reflux or SIBO?
"Acid reflux patients, SIBO (small intestinal bacterial overgrowth), or chronic bloating patients often report resolution of oral symptoms after their have been resolved," noted Dr Shukla.
"When we address conditions such as SIBO with specific antibiotics or probiotics, patients tend to feel some relief from symptoms such as a bitter taste, dry mouth, or halitosis," added Dr Shukla.
Additionally:
Acidic erosion of teeth enamel can be improved by treating acid reflux.
Healthy gums and fresher breath could be achieved by restoring gut flora with diet and supplements.
What Science Says About Gum-Gut Axis?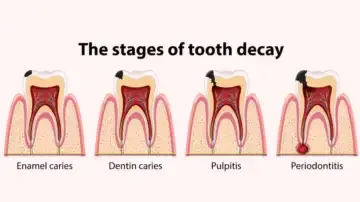
According to an emerging research by the National Library of Medicine, the inflammation associated with gum disease might contribute to systemic inflammation. In turn, this could affect other parts of the body, including the gastrointestinal tract. Gum disease-related inflammation may lead to systemic inflammation, which could then impact other bodily systems, such as the gastrointestinal tract.
Key Takeaways:
- Oral symptoms may indicate greater .
- The health of the gut influences nutrient uptake, inflammation and bacterial balance, which is essential to oral health.
- Without any effect of the regular dental care, one can approach a gastroenterologist to perform further tests.

 According to an emerging research by the National Library of Medicine, the inflammation associated with gum disease might contribute to systemic inflammation. In turn, this could affect other parts of the body, including the gastrointestinal tract. Gum disease-related inflammation may lead to systemic inflammation, which could then impact other bodily systems, such as the gastrointestinal tract.
Key Takeaways:
According to an emerging research by the National Library of Medicine, the inflammation associated with gum disease might contribute to systemic inflammation. In turn, this could affect other parts of the body, including the gastrointestinal tract. Gum disease-related inflammation may lead to systemic inflammation, which could then impact other bodily systems, such as the gastrointestinal tract.
Key Takeaways: