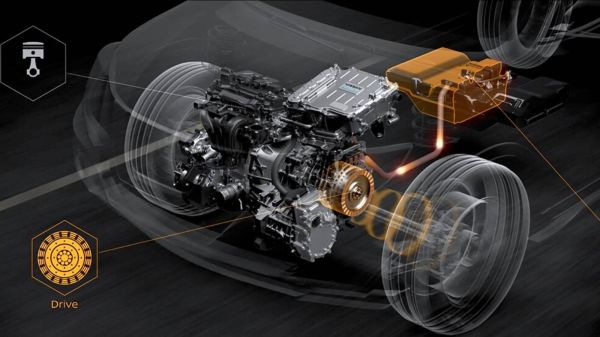
Nissan’s e-POWER is the brand’s interpretation of electrification. Introduced in Japan in 2016, this sophisticated technology sets itself apart from the competition and changes how hybrids operate. In traditional hybrids like the Ford Fusion Energi, the Range Rover PHEV, and the Toyota Prius, the internal combustion engine (ICE) and electric motor alternately drive the wheels. In the e-POWER system, on the other hand, the petrol engine works exclusively as a generator while the electric motor drives the wheels.
Advertisement
Available in vehicles such as the X-Trail and Qashqai SUVs, the e-POWER combines a 1.5-litre three-cylinder, an inverter, a 1.8 kWh battery, and an electric motor. Together, these components create a series hybrid layout, where the engine charges the battery, which powers the motor to drive the wheels. This means the car drives like a fully electric car but without the constant charging. It’s like an electric car that charges with regular fuel, as it is more focused on the electric motor than the ICE engine. But, how does the Nissan e-POWER work, and what makes it different from other systems?
How does the Nissan e-POWER work?
In the e-POWER, the 1.8 kWh high-voltage battery stores energy that’s either supplied by the engine or energy gained via regenerative braking. This battery capacity is smaller than what’s; typically found in hybrid vehicles —where capacities range between 10 kWh and 20 kWh— it serves an important purpose. Unlike other hybrids that prioritize the electric-only, range, the battery in the e-POWER focuses on optimizing a car’s efficiency. And, theoretically, it does, because the engine runs less often, but even when it starts running, it’s not operating under a lot of stress.
Advertisement
When you start up an e-POWER-equipped vehicle, the engine immediately starts sending power to the battery, keeping it charged and supplying power to the motor for acceleration. So the electric motors will continue sending power to the wheels as long as you have gas. While the electric motor is tasked with powering the wheels, the petrol engine in the e-POWER runs at a constant speed — which reduces engine- mechanical stress and fuel consumption. In this case, the engine’s output meets the demands of the electric motor and battery.
Another cool feature of the e-POWER is the electric motor’s ability to deliver instant torque and acceleration, which, interestingly, are also some of the perks of owning an electric car. And, while it doesn’t require external charging, riders can recharge it from a wall plug if needed. NIssan’s development of the e-POWER isn’t; just about being different from the rest, but it is surprisingly practical too. With characteristics that match an EV, the system delivers a pleasant driving experience. Moreover, with the e-POWER, Nissan can produce hybrids and EVs at lower costs.
Advertisement
Nissan e-POWER vs. other hybrid technologies
The Nissan e-POWER stands out from traditional hybrids and plug-in hybrids due to its unique power distribution. As mentioned, the e-POWER system uses the engine as the generator and to charge the battery, while the electric motors power the wheels. In parallel hybrid systems used by brands like Toyota and Hyundai, the engine and motor can both directly drive the wheels. With this series hybrid setup, the e-POWER hybrid system delivers a more EV-like driving experience.
Advertisement
Another key difference between the e-POWER and other hybrids lies in charging requirements. Nissan’s e-POWER eliminates the need for external charging, as the petrol engine and regenerative braking replenish the battery while driving. In comparison, PHEVs require external charging to maximize the electric-only driving range and often switch to ICE mode when the battery depletes. Other traditional hybrids operate without a charger too, but they heavily depend on the petrol engine. This can make driving them feel less smooth and electric-focused than Nissan’s system.
The electric approach gives the e-POWER several advantages, one being that the engine operates at optimal running speeds, reducing fuel consumption and CO2 emissions. Also, with features like regenerative braking in the mix, a lot of energy is captured during deceleration, which boosts efficiency. So, compared to plug-in hybrids that need charging from a wall socket, the e-POWER relies entirely on petrol to keep the system running. This makes it convenient and reduces range anxiety — which is common among EV owners.
Advertisement