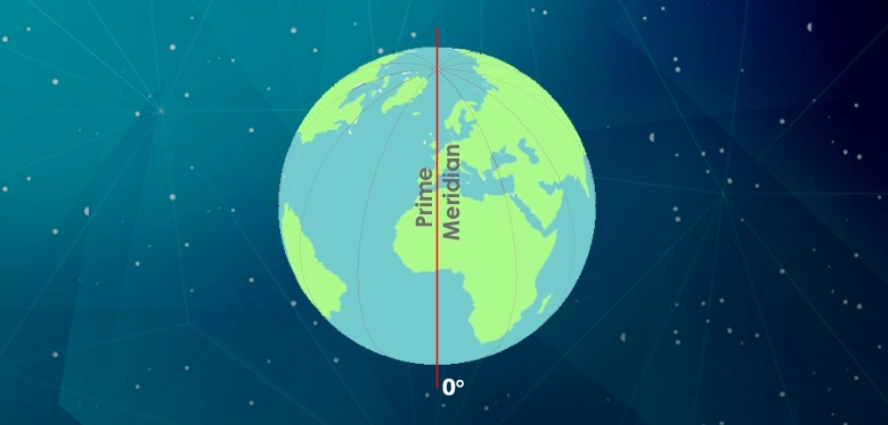
The concept of 0 degrees longitude, also known as the Greenwich Meridian, often sparks curiosity about its origins and significance. This imaginary line, stretching from the North Pole to the South Pole, divides the Earth into the Eastern and Western Hemispheres, acting as the foundation for global time measurement.
Greenwich, London, was chosen as the location for 0 degrees longitude in the 19th century. With global trade and communication booming, a standardised time system became essential.
As a leading global power, Britain hosted the International Meridian Conference in 1884. Greenwich, home to the renowned Royal Observatory, was chosen as the prime meridian, reflecting the significant influence of the British Empire.
Longitude lines, running north to south, are essential for pinpointing locations. These lines, encircling the Earth 360 degrees, measure the angular distance east or west from the Greenwich Meridian.
The importance of 0 degrees longitude is undeniable. Greenwich Mean Time (GMT), based on this meridian, sets the standard for time zones worldwide, ensuring consistency in scheduling and communication. It also plays a crucial role in navigation and mapmaking.
The Greenwich Royal Observatory, situated at 0 degrees longitude, attracts visitors from around the globe. This site marks not only a geographical reference point but also a pivotal moment in history when the world agreed on a unified system of timekeeping.